Abstract
Introduction Efanesoctocog alfa (formerly BIVV001) is a new class of FVIII replacement therapy uniquely engineered to decouple recombinant FVIII from endogenous von Willebrand factor (VWF) and overcome the VWF-imposed half-life ceiling. Once-weekly efanesoctocog alfa provides high sustained FVIII activity in the normal to near-normal range for most of the week and demonstrated superior bleed protection compared with prior FVIII prophylaxis. FVIII activity data have been collected from 5 clinical studies (Phase 1/2a single- and repeat-dose studies [NCT03205163 and EudraCT 2018-001535-51, respectively] in adults, and Phase 3 studies in adults and adolescents ≥12 years of age [XTEND-1, NCT04161495] and children ≥1 year to <12 years [XTEND-Kids, NCT04759131] and Phase 3 long-term extension study [XTEND-ed, NCT04644575]). We aimed to develop a popPK model to characterize FVIII activity after efanesoctocog alfa dosing, identify intrinsic and extrinsic factors affecting pharmacokinetics (PK), and assess PK variability.
Methods FVIII activity levels used to develop the popPK model were measured by the one-stage clotting assay from 3054 blood samples from 199 adults and adolescents and 61 children who received efanesoctocog alfa in the aforementioned studies. Body weight and VWF antigen level ranged from 12.5 kg-133 kg and 40 IU/dL-339 IU/dL, respectively. A one-compartment model with linear elimination was used to characterize FVIII activity with an estimated allometric body weight effect on clearance (CL) and volume of central compartment (V) to account for the dependence of CL and V on body size. Baseline VWF, baseline hematocrit, race (White and Asian), hepatitis C virus and human immunodeficiency virus status, and blood types (A, B, O) were tested for statistical significance in the covariate analysis. The final popPK model was used to simulate various dose regimens in a virtual population of adult and adolescent patients generated using baseline body weight distribution from the Phase 1/2a studies and XTEND-1.
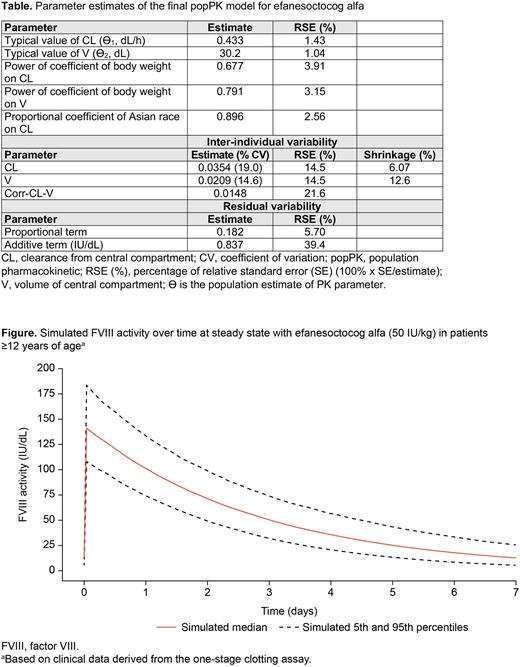
Results The final popPK model described the FVIII activity over time profile, captured inter-individual variability in FVIII activity, and precisely estimated moderate inter-individual variability in CL and V (Table). Body weight effect allometric exponents showed that absolute CL and V increase with body weight, with overall faster elimination with lower body weight. Asian race was identified as a statistically significant covariate on CL (P<0.001); CL in Asians was 10.4% lower than in non-Asians. Baseline VWF level was not identified as a statistically significant covariate in the final popPK model, consistent with prior studies that demonstrate that the PK of efanesoctocog alfa is VWF-independent. Simulated steady-state FVIII activity over time for efanesoctocog alfa is presented in the Figure. The final popPK model showed that a once-weekly efanesoctocog alfa (50 IU/kg) prophylaxis regimen achieves a steady state Ctrough of >10 IU/dL and the time to 40 IU/dL FVIII activity was 3 to 4 days in the majority of adult and adolescent patients, irrespective of body weight and race. Simulations for perioperative management during major surgery and treatment of major bleeds showed that a loading dose of 50 IU/kg, followed by 30 IU/kg every 3 days in the postoperative period, met the World Federation of Hemophilia guidelines for peak FVIII activity for most adults and adolescents. Similarly, for minor surgeries and treatment of moderate to minor bleeds, a single dose of 50 IU/kg efanesoctocog alfa resulted in peak FVIII activity that met these guidelines.
Conclusions A linear one-compartment popPK model was able to adequately characterize FVIII activity in patients with severe hemophilia A. Although CL and V depended on body weight and Asian race was identified as a covariate on CL, body weight and Asian race's limited influence on FVIII exposure was not considered clinically meaningful. PopPK simulations demonstrated that 50 IU/kg once weekly efanesoctocog alfa achieved sustained FVIII activity in the normal to near-normal range (>40 IU/dL) for 3-4 days and >10 IU/dL at Day 7 in most adults and adolescents. PopPK simulations also supported the Phase 3 dose regimens selected for regular prophylaxis, treatment of bleeds, and perioperative management.
Study was funded by Sanofi and Sobi.
Disclosures
Bhagunde:Sanofi: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company, Research Funding. Lu:Sanofi: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Demissie:Sanofi: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Willemze:Sanofi: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company. Katragadda:Sanofi: Current Employment, Current holder of stock options in a privately-held company.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal